
Land Acknowledgement: We would like to acknowledge that our University is located on Treaty 7 Territory, which is the traditional territory of the Blackfoot Confederacy, comprised of the Siksika, the Piikani, and the Kainai First Nations; the Tsuut’ina First Nation; and the Stoney Nakoda, which includes the Chiniki, Bearspaw, and Goodstoney First Nations. Treaty 7 is also home to the Métis Nation of Alberta – Region III.
References:
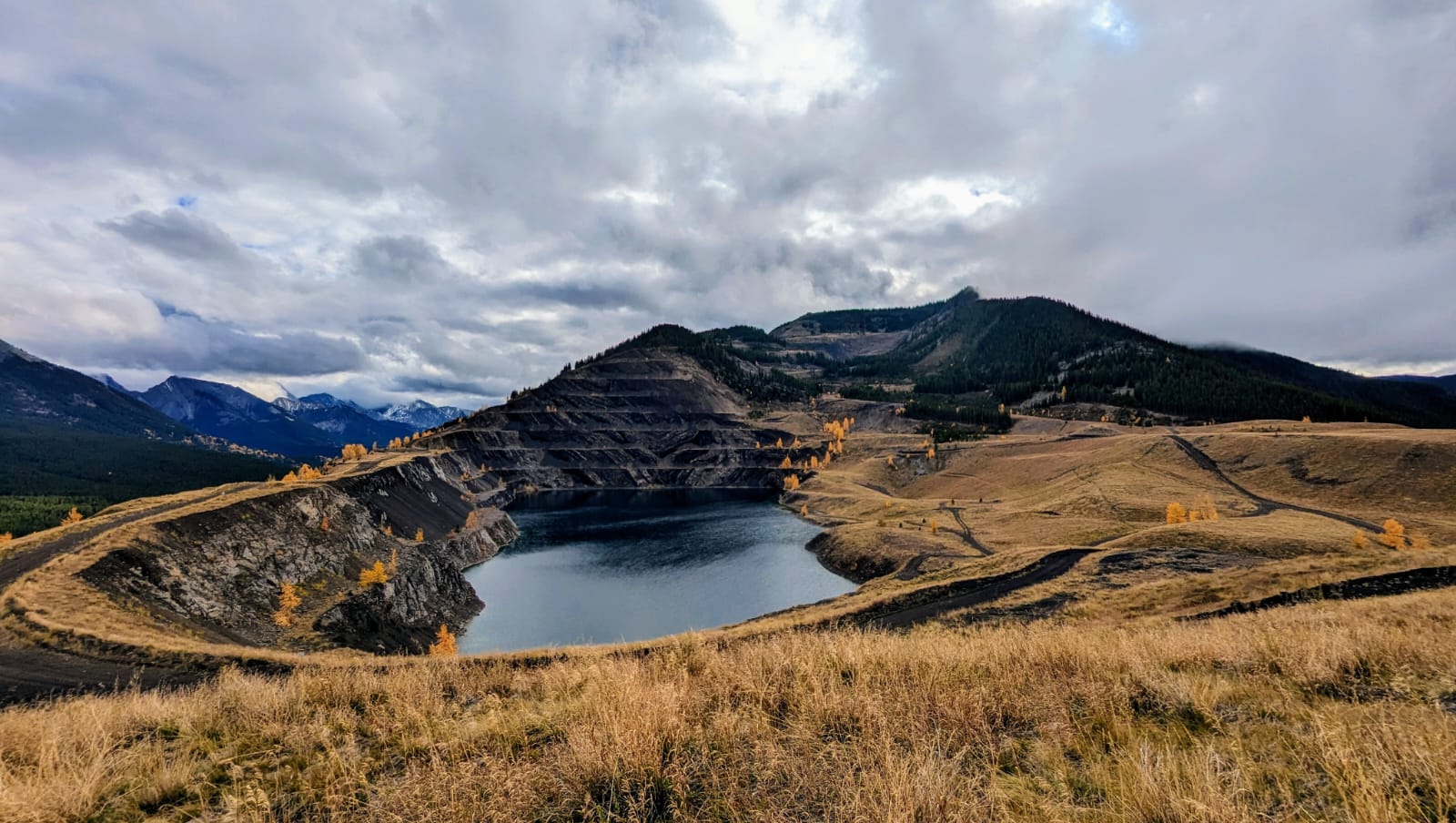
[1] Evolve Power. "Tent Mountain Pumped Hydro Energy Storage." [Online]. Available: https://evolvepower.ca/what-we-do/tent-mountain-pumped-hydro-energy-storage/. [March 23, 2024].